Creating Dashboards
There are several ways to monitor the performance of a Etn-sc node. Insights into a node's performance are useful for debugging, tuning and understanding what is really happening when Etn-sc is running.
Prerequisites
To follow along with the instructions on this page it will be useful to have:
a running Etn-sc instance.
basic working knowlegde of bash/terminal.
This video provides an excellent introduction to Geth monitoring.
Monitoring stack
An Electroneum Smart Chain client collects lots of data which can be read in the form of a chronological database. To make monitoring easier, this data can be fed into data visualisation software. On this page, a Etn-sc client will be configured to push data into a InfluxDB database and Grafana will be used to visualise the data.
Setting up InfluxDB
InfluxDB can be downloaded from the Influxdata release page. It can also be installed from a repository.
For example the following commands will download and install InfluxDB on a Debian based Linux operating system - you can check for up-to-date instructions for your operating system on the InfluxDB downloads page:
curl -tlsv1.3 --proto =https -sL https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdb.key | sudo apt-key add
source /etc/lsb-release
echo "deb https://repos.influxdata.com/${DISTRIB_ID,,} ${DISTRIB_CODENAME} stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/influxdb.list
sudo apt update
sudo apt install influxdb -y
sudo systemctl enable influxdb
sudo systemctl start influxdb
sudo apt install influxdb-clientBy default, InfluxDB it is reachable at localhost:8086. Before using the influx client, a new user with admin privileges needs to be created. This user will serve for high level management, creating databases and users.
Now the influx client can be used to enter InfluxDB shell with the new user.
A database and user for Etn-sc metrics can be created by communicating with it directly via its shell.
Verify created entries with:
Leave InfluxDB shell.
InfluxDB is running and configured to store metrics from Etn-sc.
Setting up Prometheus
Prometheus can be downloaded from the Prometheus. There is also a Docker image at prom/prometheus, you can run in containerized environments. eg:
Here a example directoy of /path/to/promethus:
And an example of prometheus.yml is:
Meanwhile, Recording rules are a powerful feature that allow you to precompute frequently needed or computationally expensive expressions and save their results as new sets of time series. Read more about setting up recording rules at the official prometheus docs.
Preparing Etn-sc
After setting up database, metrics need to be enabled in Etn-sc. Various options are available, as documented in the METRICS AND STATS OPTIONS in etn-sc --help and in our metrics page. In this case Etn-sc will be configured to push data into InfluxDB. Basic setup specifies the endpoint where InfluxDB is reachable and authenticates the database.
These flags can be provided when Etn-sc is started or saved to the configuration file.
Listing the metrics in the database verifies that Etn-sc is pushing data correctly. In InfluxDB shell:
Setting up Grafana
With the InfluxDB database setup and successfully receiving data from Etn-sc, the next step is to install Grafana so that the data can be visualized.
The following code snippet shows how to download, install and run Grafana on a Debian based Linux system. Up to date instructions for your operating system can be found on the Grafana downloads page.
When Grafana is up and running, it should be reachable at localhost:3000. A browser can be pointed to that URL to access a visualization dashboard. The browser will prompt for login credentials (user: admin and password: admin). When prompted, the default password should be changed and saved.
The browser first redirects to the Grafana home page to set up the source data. Click on the "Data sources" icon and then click on "InfluxDB". The following configuration options are recommended:
Click on "Save and test" and wait for the confirmation to pop up.
Grafana is now set up to read data from InfluxDB. Now a dashboard can be created to interpret and display it. Dashboards properties are encoded in JSON files which can be created by anybody and easily imported. On the left bar, click on the "Dashboards" icon, then "Import".
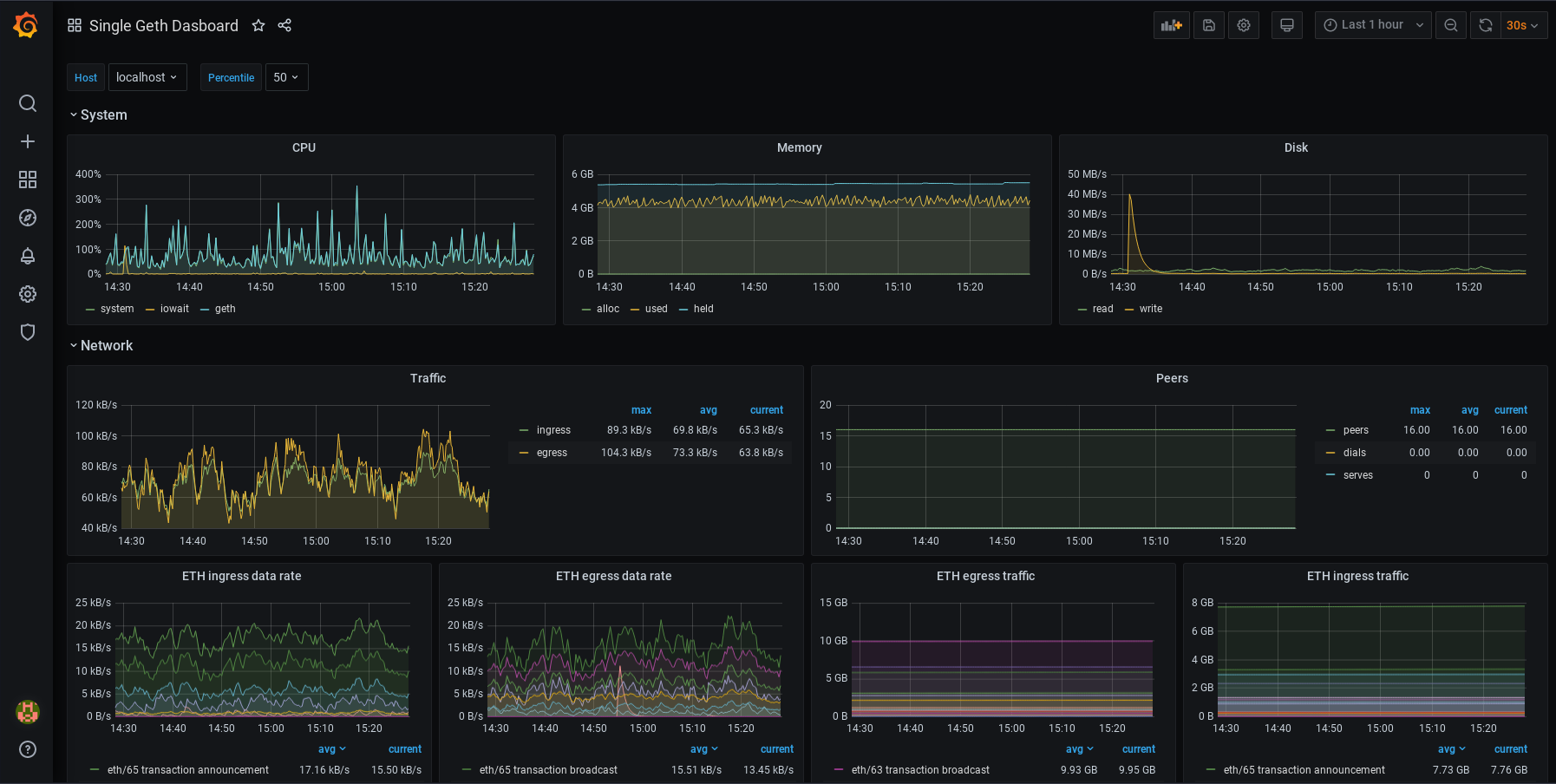
For a Etn-sc InfluxDB monitoring dashboard, copy the URL of this dashboard and paste it in the "Import page" in Grafana. After saving the dashboard, it should look like this:
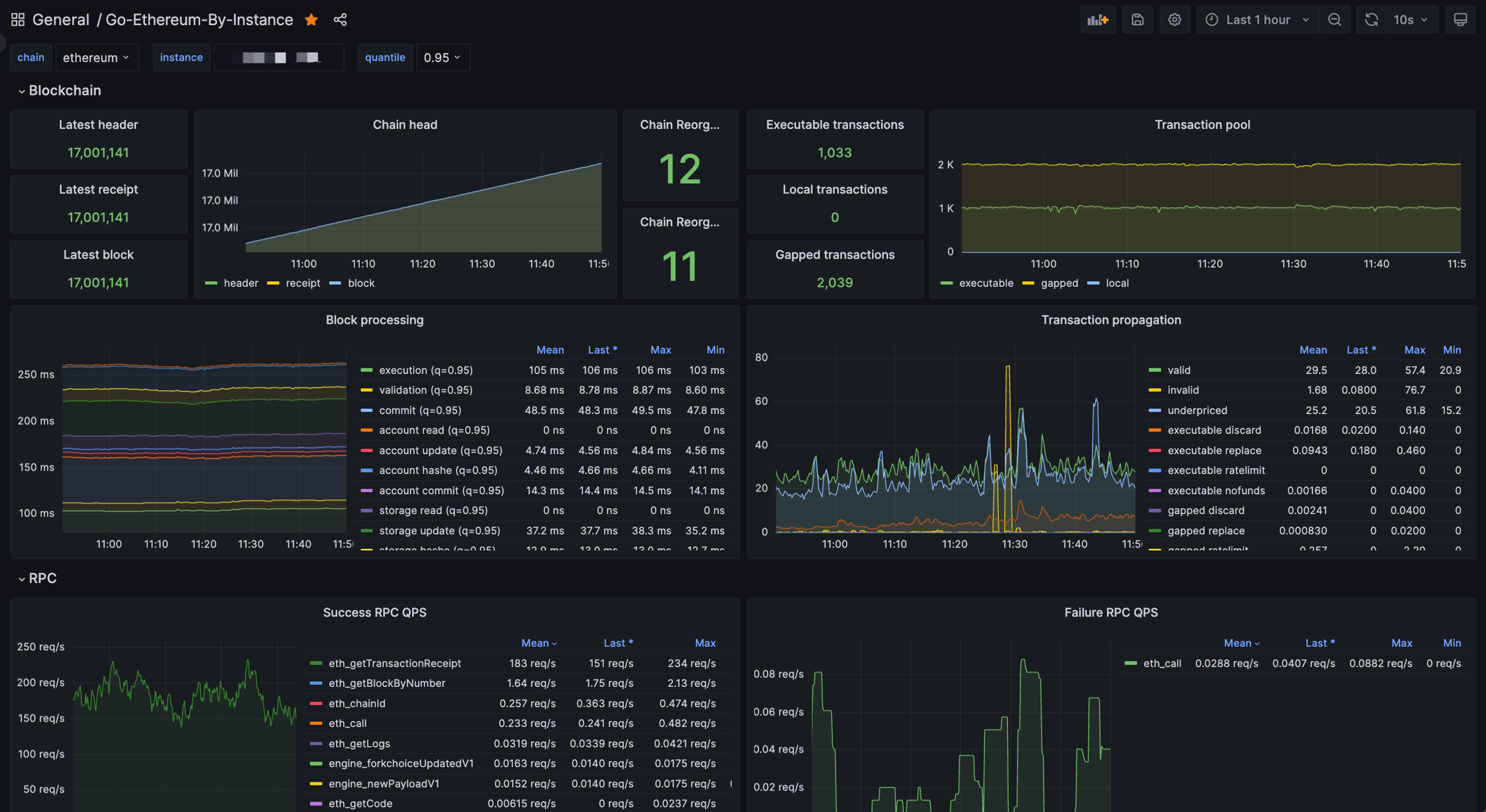
For a Etn-sc Prometheus monitoring dashboard, copy the URL of this dashboard and paste it in the "Import page" in Grafana. After saving the dashboard, it should look like this:
Customization
The dashboards can be customized further. Each panel can be edited, moved, removed or added. To learn more about how dashboards work, refer to Grafana's documentation.
Some users might also be interested in automatic alerting, which sets up alert notifications that are sent automatically when metrics reach certain values. Various communication channels are supported.
Summary
This page has outlined how to set up a simple node monitoring dashboard using Grafana.
NB: this page was adapted from a tutorial on ethereum.org written by Mario Havel
Last updated
Was this helpful?